One of the new directions for Teigha is the cloud. With Teigha Cloud, people can work with drawings remotely from any place — home, office, restaurant.
Teigha Cloud consists of the following architecture:
-
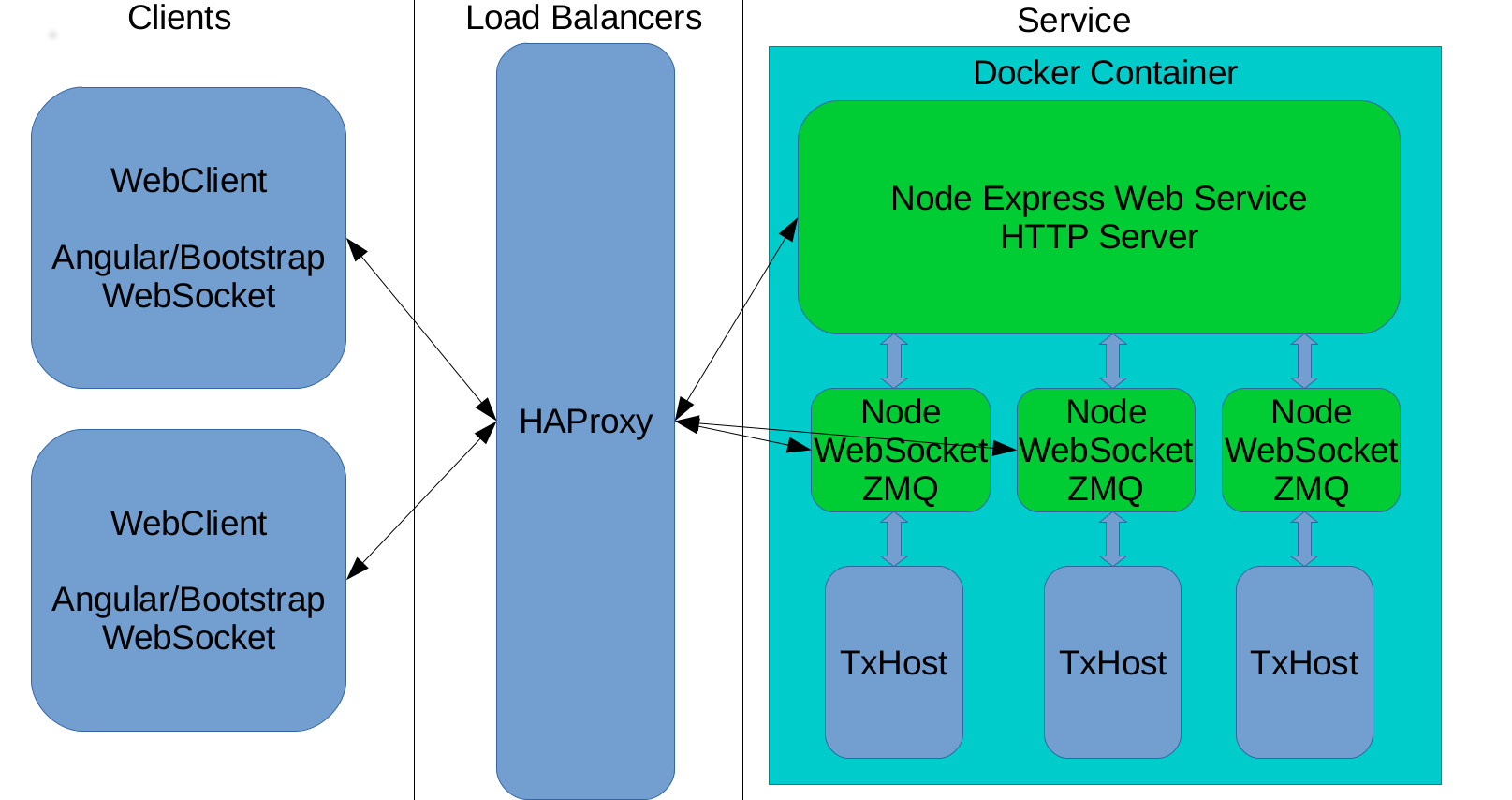
Client (Browser)
The client side renders geometry. The client makes the authorization process over HTTP/HTTPS. Then the user can access previously uploaded drawings and can upload new ones for their account. All geometry that the client receives is over a web socket connection, and this solution lets Teigha Cloud avoid a pulling model to get data from a server.
-
Load Balancer
Currently Teigha Cloud uses HAProxy, which satisfies requirements for this stage of the Teigha Service evolution. Teigha Cloud can create sticky sessions based on cookies to attach to a certain server, which allows for implementation of drawing features. To check server availability, HAProxy is configured to use a round-robin algorithm to assign new connections to servers.
-
Server
The server is the most complicated and important part of the service. The server part is based on the Node + Express library. Each service runs several Node processes (based on CPU count). Each Node Process has its own web socket connection with a client, which is best for CPU utilization. TxHost is the workhorse. This module generates all graphics and can interpret commands from clients. TxHost is written in C++ for performance reasons. Communication between the Node and TxHost processes uses ZMQ.
So, this is a short scheme of the Teigha Cloud service. More details about Teigha Cloud components coming soon.